Introduction
In the competitive business environment organisation needs to make the right decision for the organisation to get the competitive advantages. Management Accounting Systems gives the important and relevant business information to the organisation so that they can make the right financial decision. Managerial accounting helps organisation to formulate the business strategy and prepare the budget for the organisation (Copeland, 2000).
On the other hand financial accounting helps organisation to keep the data, record the information for future use. Financial accounting provide financial information and management accounting analyse the financial information to make the right decision.
In response to budget retargeting, both organizations have perception on different basis. If comparing with previous year, it is seen that organizational expenditures is increased for home furniture limited. In that case, home furniture limited may use various kind of budget like financial budget or operation budget. In addition to this, net lax liability calculation is essential for company, partnership business or single entity business ad it could be managed by tax accounting system (Weygandt, 2018).
Define Management Accounting and Requirement of different types of Management Accounting Systems
Definition of management accounting
Accounting information that is used to make the management and financial decision of the organisation is known as management accounting. Management accounting information is used by the top management of the organisation, board of directors to make the managerial and strategic decision (Copeland, 2000). Management accounting always analyse the financial accounting information and provide the meaningful and relevant information to each and every organizational department for taking right decision at right time.
Main functions of Management accounting:
Formulate the strategy: Management accounting analyse the financial information and compare the information with previous year and predict the future. Management accounting provides all the financial information to the organisation that helps organisational management people to formulate the organisational strategy (Bros, 2000).
Control the organisational operation: Management accounting provides all the information to the top management and it helps organisation to prepare budget and this things helps organisation to control their expenditures. Management accounting also helps companies to manage their financial activities in more organised way (Bros, 2000).
Evaluate the organisational performance: Managerial accounting helps organisation to compare their previous financial performance with the current one (Bros, 2000).
Financial accounting system:
Financial accounting system helps organisation to keep their financial records in the system and prepare the books of the accounts on the basis of accounting standards and maintain the international financial reporting standard (Bros, 2000). The main purpose of financial accounting is to keep the record of financial transaction and prepare the books of the account. Financial accounting is the book keeping accounting system.
Management accounting system: This is the process where managers analyse the financial information and create relevant and meaningful information for the organisation (Bros, 2000). The main purpose of management accounting is to provide the right information to make the right decision of the organisation.
Cost accounting system: It is the process of determining the costs of the particular product or service for the specific period of time. The main purpose of this accounting system is to find out the different costs of the product such as- fixed costs, direct costs, variable costs etc. There are two types of cost accounting method that most of the organisation follows such as- absorption costing method and marginal costing method (Bros, 2000).
Methods used for Management Accounting Reporting
There are different types of reporting system that organisations are used to make their plan, decision, organise and evaluate their financial performance. In the following part of this study researcher is going to explain the different management accounting reporting methods-
Budget: Budget is the most popular method that most of the organisation prepares to manage their organisation and to analyse their financial performance. Budget helps organisation to manage their organisation, control their costing and compare their actual performance with Budgeted amount. If there is any discrepancy then organisation can take the corrective action. Budget report is used in all types of organisation (Kihn and Ihantola, 2011).
Account receivable aging report:
This kind of report is used to analyse the unpaid length of time while it is sold in accrued bymanagement accountant. To prepare aging accounting receivables by the management accountant is required to prepare report in case credit analysis and management accountant use this report for adjusting of credit analysis. This report is very essential to execute credit policy (Kihn and Ihantola, 2011).
Cost managerial accounting report: This kind of report basically interpret the cost of manufacturing of each product for specific time. This report is basically the highlights of all costs which is involved in manufacturing of product. This type of report is necessary for managerial accountant for ascertaining costing, determining costing, setting up sales price and also determining profit margin (Kihn and Ihantola, 2011).
Performance Report: Management accountant used this kind of report for analysing and reviewing the organisation’s performance on department basis performance or as a whole. This kind of report is very helpful for management accountant as they can prepare strategic policy and set the strategic action plan (Kihn and Ihantola, 2011).
Management Accounting Technique
Cost:
Resources or the money that organisation need to sacrifices to manufacture product or service is known as cost. Every company need to spend money to operate their organisation. Organisations have different types of costs such as- fixed costs and variable costs. Every company should try to reduce their level of costs to increase their operational profit.
Different types of costs are discuss in the below-
Fixed and variable cost:
Fixed cost remains constant and it has no effect on activity changes. Rent expenses, salary expenses, insurance expenses, interest expenses, property tax are the example of fixed costs. On the other hand, variable cost does not remain constant and it has the effect on the changes of level of activity that means if the level of activity is changed then the variable cost is also changed. Variable cost is basically fluctuate with the changes of level of activity as this cost is varies with every unit. Direct labour, direct material are the example of variable cost and it is the nature of variable cost that while it is increasing or decreasing production level (Lakmal, 2014).
Direct and indirect cost:
Direct cost is that kind of cost which is directly related with production. So, direct cost is directly attributed to the final product. Direct labour, direct material is also the example of direct cost which is very similar to variable cost. Indirect cost are those kind of cost are related to production indirectly and these cost are indirectly attributed to manufacture final product. Rental expense, interest expense, and salary expense those are similar to fixed cost that is why indirect cost is also called fixed cost (Lakmal, 2014).
Product cost and period cost: Product cost is the cost of producing product that is included with the cost of direct cost of material and direct cost of labour. Period cost will not be included with product cost because the cost of sales commission are considered as period cost as well as advertising cost is also considered as period costs. The nature of period cost is that this cost is recorded in income statement when the cost is incurred (Lakmal, 2014).
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost is termed as the cost of choosing as well as selecting the best alternatives among the different sources and it is considered as the value of benefit that would be forgone for choosing as well as selecting best alternatives (Lakmal, 2014).
Marginal cost and absorption costing: In case of decision making process, the costs method like absorption costing and marginal costing are used. The nature of marginal costing is that it changes with the level of activity changes. Marginal costing does not include all the costs but absorption costing considers all the manufacturing cost which is included as direct labour, direct material, fixed manufacturing overhead cost and fixed manufacturing overhead cost (Lakmal, 2014).
Marginal costing method:
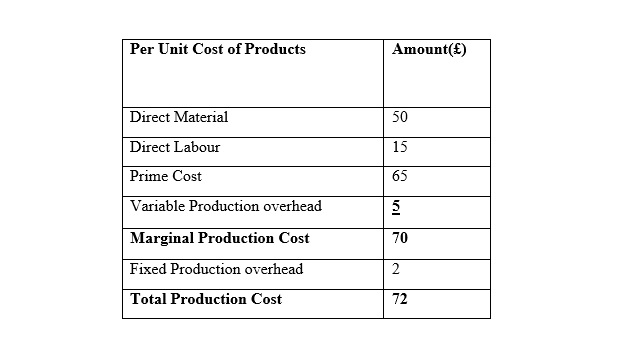
Income statement using the Marginal costing method:
Home Furniture Ltd.
Income statements for the month of January
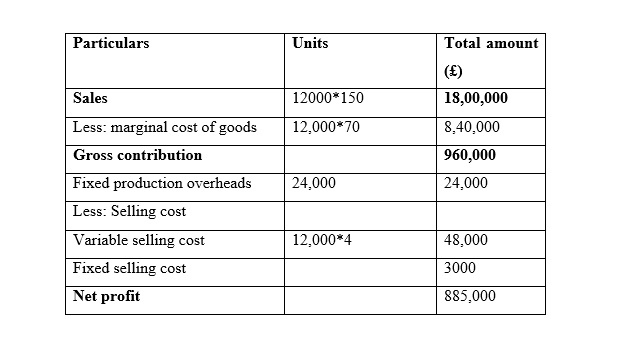
Home Furniture Ltd.
Income statements for the month of February
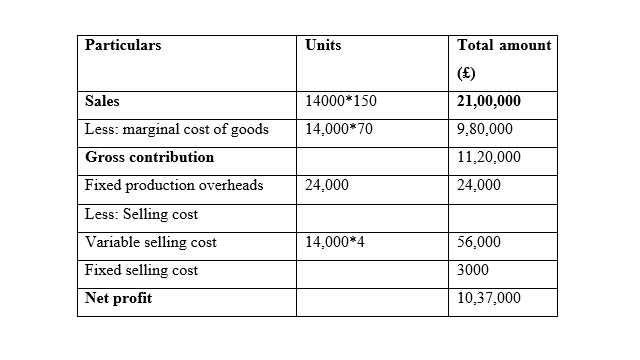
Home Furniture Ltd.
Income statements for the month of March
A cost card using Absorption costing method:
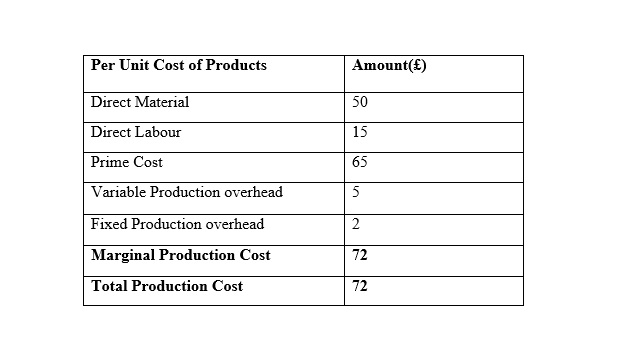
Income statement using the Absorption costing method:
Home Furniture Ltd.
Income statements for the month of January
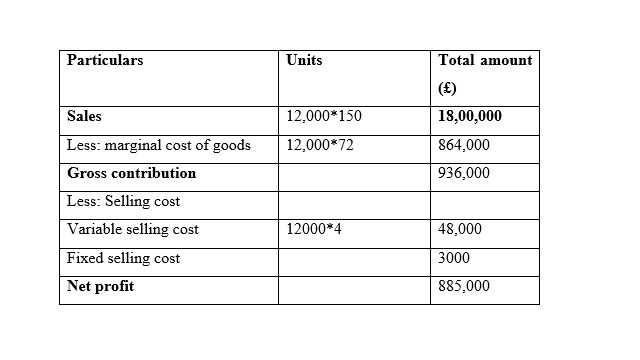
Home Furniture Ltd
Income statements for the month of February
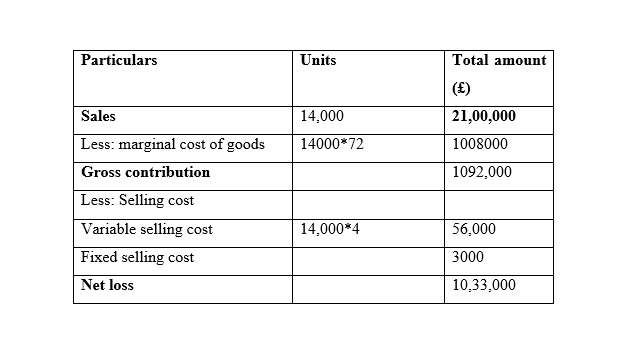
Home Furniture Ltd
Income statements for the month of March
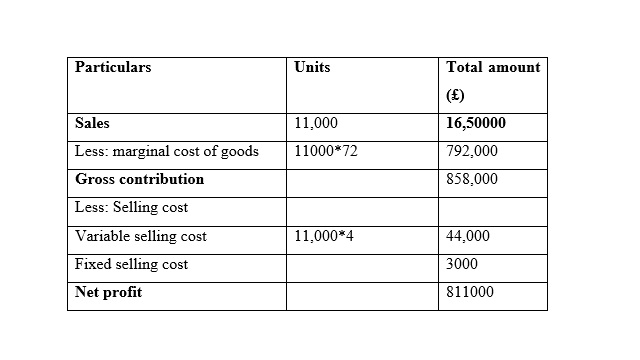
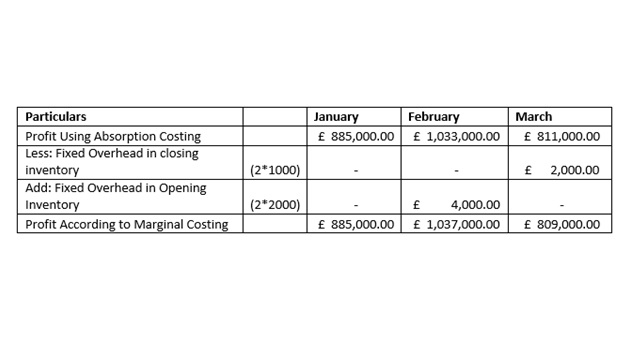
A reconciliation of absorption and marginal costing profits:
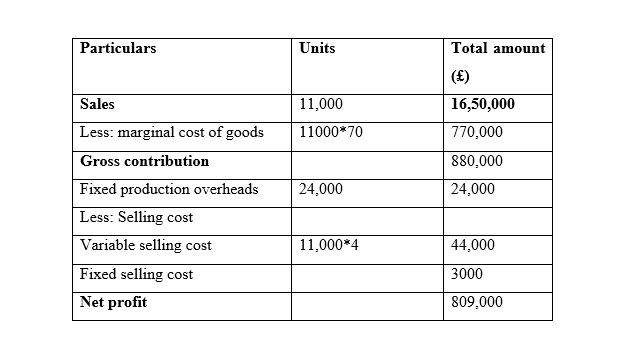
It is seen that in the month of January the Net Profit is very similar while using marginal costing and absorption costing, and the reason behind this similarity is that the sales and production for both methods are same. In addition to this, it is seen that net profit is increased while is it considered the method of marginal costing method in the month of February. Moreover, it is seen that net profit is increased while is it considered the method of absorption costing method in the month of March because unit of production is less than unit of sales (Lakmal, 2014).
Budget: Budget is considered as the numerical financial plan and it is designed for a specific time period. Budgetary control is determined by the organisation to analyse the financial activities and to forecast activities of future concerns connected to previous summary results (Titopoulou et al., 2017).
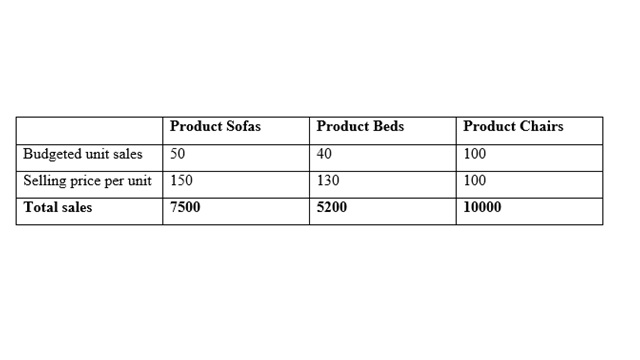
Home Furniture Ltd
Sales Budget
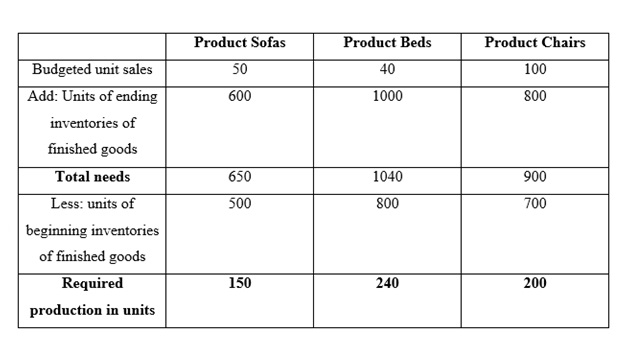
Home Furniture Ltd
Production Budget
Home Furniture Ltd
Material usage budget
| Particulars | Unit | Wood | Varnish | |||||
| Wood | Varnish | Sofa | Bed | Chair | Sofa | Bed | Chair | |
| Budgeted Production in Unit | 150 | 240 | 200 | |||||
| Requirements of Material | ||||||||
| Product – Sofa | 12 | 4 | 1800 | 600 | ||||
| Product – Bed | 10 | 4 | 2400 | 960 | ||||
| Product – Chair | 5 | 2 | 1000 | 400 | ||||
| Material Used (Unit) | 1800 | 2400 | 1000 | 600 | 960 | 400 | ||
| Total Unit | 5200 | 1960 | ||||||
Home Furniture Ltd
Material purchase budget
| Particulars | Unit | Wood | Varnish | |||||
| Wood | Varnish | Sofa | Bed | Chair | Sofa | Bed | Chair | |
| Budgeted Production in Unit | 150 | 240 | 200 | |||||
| Requirements of Material | ||||||||
| Product – Sofa | 12 | 4 | 1800 | 600 | ||||
| Product – Bed | 10 | 4 | 2400 | 960 | ||||
| Product – Chair | 5 | 2 | 1000 | 400 | ||||
| Cost Per Kg | £ 8.00 | £ 4.00 |
|
|||||
| Cost of Material Used | £ 14,400.00 | £ 19,200.00 | £ 8,000.00 | £ 2,400.00 | £ 3,840.00 | £ 1,600.00 | ||
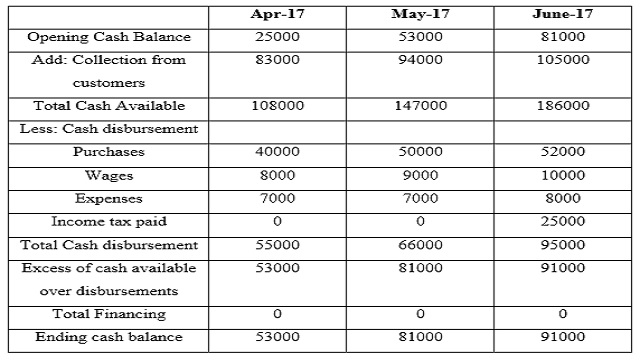
Home Furniture Ltd
A cash flow forecast
Case -5
- Flexible Budget
| Particulars | 8000 | |
| Per Unit Cost | Total | |
| Material | 70 | £ 560,000.00 |
| Labor | 25 | £ 200,000.00 |
| Prime Cost | 95 | £ 760,000.00 |
| Variable Factory Overhead | 20 | £ 160,000.00 |
| Fixed Factory Overhead (£1,00,000) | 12.5 | £ 100,000.00 |
| Total Production Cost | 127.5 | £ 1,020,000.00 |
| Variable Expense | 5 | £ 40,000.00 |
| Selling Expense | ||
| Fixed | 1.63 | £ 13,000.00 |
| Variable | 11.7 | £ 93,600.00 |
| Distribution Expense | ||
| Fixed | 1.75 | £ 14,000.00 |
| Variable | 5.6 | £ 44,800.00 |
| Administrative Expense | 6.25 | £ 50,000.00 |
| Total Cost | 254.43 | £ 2,035,400.00 |
- Variances between actual and flexible budget
| Particulars | 8000 | 10000 | ||
| Per Unit Cost | Total | Per Unit Cost | Total | |
| Material | 70 | £ 560,000.00 | 70 | £ 700,000.00 |
| Labor | 25 | £ 200,000.00 | 25 | £ 250,000.00 |
| Prime Cost | 95 | £ 760,000.00 | 95 | £ 950,000.00 |
| Variable Factory Overhead | 20 | £ 160,000.00 | 20 | £ 200,000.00 |
| Fixed Factory Overhead (£1,00,000) | 12.5 | £ 100,000.00 | 10 | £ 100,000.00 |
| Total Production Cost | 127.5 | £ 1,020,000.00 | 125 | £ 1,250,000.00 |
| Variable Expense | 5 | £ 40,000.00 | 5 | £ 50,000.00 |
| Selling Expense | ||||
| Fixed | 1.63 | £ 13,000.00 | 1.3 | £ 13,000.00 |
| Variable | 11.7 | £ 93,600.00 | 11.7 | £ 117,000.00 |
| Distribution Expense | ||||
| Fixed | 1.75 | £ 14,000.00 | 1.4 | £ 14,000.00 |
| Variable | 5.6 | £ 44,800.00 | 5.6 | £ 56,000.00 |
| Administrative Expense | 6.25 | £ 50,000.00 | 5 | £ 50,000.00 |
| Total Cost | 254.43 | £ 2,035,400.00 | 250 | £ 2,500,000.00 |
| Variances between actual and Flexible budget | £ 464,600.00 | |||
Advantages and disadvantages of different types of planning tools used for budgetary Control
Incremental budgeting:
Incremental budgeting is used by home furniture limited to allocate different resources which is basically depends on the existing resources operations. The nature of incremental budgeting is traditional budgeting system. This kind of budgeting is used as well as applied in small organisations because in this organization the allocation of resources allocation is not properly connected to level of activity. Incremental budgeting is used by home furniture limited to represent the under the headings of functional criteria as it may focus on costing nature (Titopoulou et al., 2017).
Activity based budgeting: It is considered as the sophisticated budgetary control or the sophisticated budgetary techniques where the allocation of resources is properly connected to strategic plan as well as strategic action in response to the consideration of alternative strategy (Titopoulou et al., 2017). This kind of budgeting technique may increase new activities as it would be easy to gain strategic goals as well as budget goals. This kind of budgeting emphasizes on the process of output rather than process of input. It is a total framework of budgeting that helps to make the connection between level of activity and level of costs.
Zero based budgeting: It is such kind of budgetary control that may be needed of each and every unit of elements and it is to be justified during the time of start-up. It allows the budgeting system where the allocation resources is utilized properly among the activities of competitive aspects without considering the aspects of money (Titopoulou et al., 2017). This type of budgeting is related to decision making purpose if it is to compare with incremental budgeting. The forms of zero based budgeting is used to make the rank of every activity level as it may be easy for taking separate decision where the available sources are allocated.
Value based budgeting: It is considered as the emerging tools used for maintaining budgetary control. It is used in whole budget process that may add some value in every functional department or the organization as a whole (Titopoulou et al., 2017).
How organizations are adapting management accounting system to respond financial crisis
Business organization have to face so many challenges in operating as well as running business in this modern business times. There are sever competition among the firms for leading the market share, for increasing the sales, for increasing customer size or for controlling the cost to take the advantage of cost leadership. To deal with these faced challenges or to overcome those challenges each and every company need accurate information as it will help them to take correct decision. Management accounting system is the tools for collecting information for decision making and it is termed as an integrated accounting system for the professional management accountant for decision making purpose on right time and the usage of it is widely accepted globally by the management accountant because it is more helpful for them to deliver accurate decision when the situation is hard or the situation of emergency (Cooper, 2006). So, it is recommended for home furniture limited to use as well as utilize the benefits of budgetary control to make the right decision to operate the business smoothly and the scenario of benefits is very similar for Sewport limited to use the budgetary control tools for meeting up the organisational target.
It is seen that home furniture limited is using budgetary control tools and techniques very carefully for their valuation of performance, but the scenario is different in the case of Sewport limited for the aspect of adaptation policy.
Key financial performance indicators used by Home Furniture Ltd
| Key Performance Indicators | Effects |
| Liquidity Ratio | He use liquidity ratio used by home furniture ltd to measure the ability of the company in terms of converting its assets in to cash to meet up their short term obligations (Langer, 2009). So, Home furniture limited is able to meet up its short term obligations as it has the ability to covert its asset into cash when it is required for them. |
| Profitability Ratio | The profitability ratio is used by home furniture ltd to measure operating ability as they are able to meet up operating expenses (Langer, 2009). |
| Horizontal Analysis | The horizontal analysis used by home furniture ltd to evaluate financial performance over a time horizon as they are able to maintain financial stability (Langer, 2009). |
| Segment reporting | The segment reporting is used by home furniture ltd to measure operating ability of specified segment with segment margin as they are able to earn segmented profit (Langer, 2009). |
Key financial performance indicators used by Sewport Ltd:
| Solvency ratio | The solvency ratio used by Sewport Ltd to measure its capability to evaluate the survival factors for long period as it may focus on the ratio of debt to total asset to assess the asset amount provided to creditors (Langer, 2009).
|
| Vertical analysis | The vertical analysis used by Sewport Ltd to evaluate the financial performance by representing its financial statement considering the base amount (Langer, 2009). |
| Earnings per share | The earnings per share used by Sewport Ltd to measure net earnings for every common stock holders (Langer, 2009). |
| Economic Value added | The Economic Value added used by Sewport Ltd to measure capacity in terms of value addition (Langer, 2009). |
Non-financial key performance indicators:
| KPI | Effects |
| Competitiveness | The techniques of competitiveness is used as non-financial performance indicator as a parameter of sales growth customer size, service size, market size to measure market competitiveness (Langer, 2009). |
| Activity level | It is used as non-financial parameter to measure as well as evaluate performance of per unit sales, labour hours and machine hours etc (Langer, 2009). |
| Productivity | It is used as non-financial performance parameters to measure capacity utilisation for new operating production (Langer, 2009). |
| Quality of service | It is used as non-financial performance parameters to measure or evaluate per unit sales rejected during the process of manufacturing or servicing (Langer, 2009). |
Budgetary Targeting:
In terms of analysis, both organizations have different perceptions for retargeting the budget (Jacobs, 2003). If considering the context of current market scenario of home furniture limited expenditures as well as the organizational expenditure is increasing compare to the time of previous period. So, it will be beneficial for home furniture ltd. to use different kinds of budget like financial budget or operation budget.
Comparatively, the context of current market scenario of Sewport limited are not able to deal with effective liquidity where they are not able to meet up their short term obligation as they have problems in using cash budget and ultimately they failed avoid liquidity crisis.
Benchmarking analysis: It is recommended to use the benchmarking practice by Home furniture limited as they can do their continuous improvement (Jacobs, 2003).
Comparatively, it is recommended to analyse the whole market to uncover hard as well as toughest area Sewport limited.
Conclusion
As an integrated accounting system, the aspect of management accounting system is interrelated with business information and accurate decision making from those accurate information (Weygandt, 2018). It is the fact that the execution as well as usage of professional management accountant is increasing in recent times. The reason behind this is that it helps to take accurate decision in any situation of business emergency. So, it is recommended for home furniture limited to use budgetary control tools for successful business operation and the scenario is also same to recommend the same for Sewport limited to meet up organisational targets. In most recent scenario of home furniture limited is using the budgetary control tools more carefully for evaluating business performance which is different in Sewport limited for adaptation (Jacobs, 2003).
References
Bros, A. (2000). Management Accounting and Main functions of Management accounting. Management Accounting Research, 11(1), p.167.
Cooper, P. (2006). Adapting management accounting knowledge needs to functional and economic change. Accounting Education, 15(3), pp.287-300.
Copeland, R. (2000). Managerial accounting. Houston, TX: Dame.
Jacobs, J. (2003). Budgeting and Budgetary Control. SSRN Electronic Journal, 2(1).
Kihn, L. and Ihantola, E. (2011). Reporting Methods in Management Accounting Field Research. SSRN Electronic Journal, 24(4).
Lakmal, D. (2014). Cost Analysis for Decision Making and Control: Marginal Costing versus Absorption Costing. SSRN Electronic Journal, 4(1).
Lanen, W., Anderson, S. and Maher, M. (2019). Fundamentals of cost accounting. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Langer, J. (2009). Key financial performance indicators. Financial Abstracts, 54(5), p.232.
Titopoulou, M., Ganeva, R., Staykova, J. and Titopoulos, E. (2017). Advantages and disadvantages of different types of planning tools used for budgetary control. European Journal of Economics and Business Studies, 7(1), p.199.
Weygandt, J. (2018). Managerial Accounting. New York: Wiley.
Written by
Email: [email protected]
