Employees Motivation of Tesco
Motivation is the way used to make the employees dedicated and boost up their mindset by using some tactics of human resource management. It is one of the most important functions of managers. By motivating the employees it is possible to increase the overall outcome and betterment of the organization and achieve their goals by improving the service standards (Leroy et al., 2018).

Managers use different types of motivational tools to encourage their employees to increase their self-confidence and dedication towards their job. The most common method is providing rewards to the employees and the benefit they get from employees are:
- Employees perform well and increase their productivity
- Motivated workers develop long term relationship with loyal customers and their organization
- They can participate in organizational decision making and become better assets of any organization (Kramar and Syed, 2012).
Managers are dedicated to using different theories of Motivation developed by the researchers based on the need of the organizations. Here are two motivational theories are explained which are used in Tesco’s operation and quite successful in the organization.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
The most traditional, well known and commonly used motivation theory is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs developed based on the 5 basic needs of human life and they are:
- Physiological Needs: Physiological needs are the basic requirements of food, shelter, treatment, and cloths. People who cannot fulfill these needs Tesco try to provide them work and ensure their needs with their salary and other incentives (Leroy et al., 2018).
- Safety needs: In this stage, people search for job security, safety, and a better way of living. Here Tesco ensures their job security and provides them comfort to perform well to ensure their security with their performance.
- Social needs: After physiological and safety need social acceptance and recognition become important to employees. So providing them appreciation and recognizing their works it is possible to ensure their social needs (Kramar and Syed, 2012).
- Esteem needs: Esteem need is one of the highest levels of needs to fulfill their dreams and desire for having a big house, expensive cars, and luxury clothing. Here people interact and communicate with their family, friends, and more people to satisfy their esteem (Leroy et al., 2018).
- Self-actualization needs: The highest and final stage of people’s needs is self-actualization needs. People can achieve such kind of need fulfillment with their work for the country or people. So here they concentrate on something memorable for everyone by creating an example.
Tesco tries to provide its employees with a better salary and yearly bonus based on their improved performance. Primarily they try to meet the employee’s physiological and safety needs (Leroy et al., 2018). Then Tesco focus on ensuring a better working environment, providing work-life balance; promote the health and safety of the work, and their health. They also make their employees’ jobs are permanent after a certain time. The organization is very concerned about their employee’s safety, health, and other concerns they are facing in regular life and tries to minimize their anxiety as much as possible by fulfilling their social needs. For the esteem and self-actualization need they provide formal and informal support in many ways from Tesco’s point of achievement (Kramar and Syed, 2012).
Advantages
- Easy and effective theory to apply and understand employees.
- It has close relevance to the employee’s life and their improvement.
Disadvantages
- Varies from person to person, so not always provide the best outcome (Leroy et al., 2018).
- It’s hard to predict how far esteem and self-actualization need leads the employees and organization.
Herzberg two factor theory of Motivation
Another very popular motivation theory is known as Herzberg’s two-factor theory. Here, Herzberg divided the motivation factors in two ways- Motivators and Hygiene factors, and they are explained as follows based on Tesco’s strategy of using them.
Motivators: Motivators are some factors that are necessary to ensure the motivation of the employees but they are not actually mandatory for employee’s motivation. They don’t have any direct relation to motivating employees but their absence can create dissatisfaction in the job (Kramar and Syed, 2012). So by offering them Tesco increase their job satisfaction level and ensure their dedication and commitment for the organization.
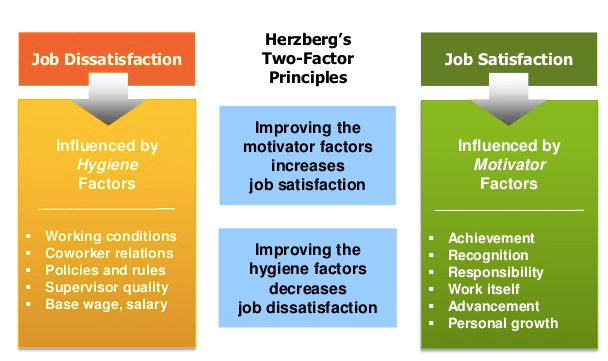
Figure: Herzberg’s Two-factor Theory
Hygiene factors: Hygiene elements are a must for ensuring employee’s motivation and boost up their energy. Because their absence can lead the employee’s unable to perform well in the long run. Salary, friendly working environment, supportive teammates are some important elements of hygiene factors (Kramar and Syed, 2012). Unavailability of these factors can lead to serious damage in the working environment for the employees’ overall mindset.
So, Tesco tries to offer both hygiene and motivators factors to enable the employees with their perfect workplace support and try to get the best outcome from them whenever necessary.
Factors that affect individual behavior at the workplace
Each and every employee working patterns are different from each other. Some are highly dedicated and motivated to perform and some are performed depending on their productivity level or their timings (Ivancevich and Konopaske, 2013). Some are not all ready to perform and become ineffective to add value for the organization. In the case of Tesco, there are diversified employees poll can be seen. So to understand each and every employee based on their individual behavior at the workplace method developed by Mars can be used. He has invented 4 different factors to analyze it and they are:
- Motivation
- Individual ability to perform
- Role-playing and
- Situational factors
Organizations need to understand the factors and manage them effectively to develop the individual performance of the employees on different levels. Tesco follows this model to improve its employee’s working performance and efficiency.
Motivation: Motivation is the prime need for the employees to ensure their best performance for the organization. Tesco believes that by keeping the employees happy and motivated they can get a better outcome from their employees. The Mars model used by Tesco to make the employees loyal to Tesco and perform according to their guidance (Hook and Jenkins, 2019).
Individual Ability: To improve the individual ability of the employees Tesco provide them training and take skill improvement session to fulfill their need for learning and improvement. If an employee doesn’t have the required skills it is possible to decrease their efficiency and dedication towards works (Ivancevich and Konopaske, 2013). So Tesco always makes sure that its employees are not lacking any skills and capability required for their performance.
Role Plays: Role perception and clarifies the role and responsibility can ensure a better outcome for the organization. Most of the employees are not properly about their roles and responsibilities. So to reduce their problems Tesco arranges an induction program and clarifies all the job roles related to each and every performer (Hook and Jenkins, 2019).
Situational factors: Apart from all the things discussed above there are some situational factors such as; working environment, teammates, and family problems that can also affect the employees’ performance sometimes.
Effective teamwork in the workplace
To ensure effective teamwork it is important to align their individual goals with organizational goals. So Tesco develops and motivates the teams in such a way so they can easily focus on their job roles and reach their desired success. Tesco motivates its employees to develop good relations with their colleagues for making a better team. They provide their employees’ facility to communication, trust, and share their values and opinion with each other for the organizational betterment (Blum and Wall, 1997). Here some of the ways are discussed which can be used to develop teamwork by using Tuckman’s model.
Forming: Forming is a way of making employees learn to perform their job and the skills and abilities they required to perform. Here most of the employees try to learn and acquire the knowledge as much as possible for their own betterment.
Storming: Storming is the process of making employees acquainted with each other and build up a friendly working relationship with them. Managers or leaders provide them directly to solve problems and conflicts and sort them out for performance improvement (Blum and Wall, 1997).
Norming: In case of norming employees become aware of their jobs and responsibilities and focus on individual performance as well as the group performance to achieve the organizational goal. Tesco influences its people to perform better and providing their best effort.
Performing: In performing stage employees perform their tasks to fulfill the need and requirements of the organization and individually ensure organizational needs and demands to meet up the Tesco’s expectations from them.
Conclusion
Tesco is one of the best supermarkets who take care of their employees and support them in each and every way possible. They provide financial and non-financial incentives to keep them motivated and always try to recruit best-skilled people for better performance assurance (Blum and Wall, 1997). The organization also provides training and learning sessions to develop their skills and capabilities. Overall they are careful and concern about keep their people happy to get the best outcomes from them in the long run.
References
- Barnes, R. (2011). The great Tesco beauty gamble (the Tesco supermarket chains marketing strategy for breaking into the UK beauty services market). Strategic Direction, 27(7).
- Karen (1993). NHS market gets me a job down at Tesco. Nursing Standard, 8(4), pp.41-42.
- Meighan, M. and Meighan, M. (2000). Induction training. London: Kogan Page.
- Seibert, T. (1990). Foraging on insect mutualists by the thatching ant Formica obscuripes: Interspecific and intraspecific mechanisms and implications. Urbana, IL.: University of Illinois.
- Smith, J., Connor, D., Bose, A. and Burton, E. (1985). Developemnt of Operator Training Curricula Using the Instructional Systems Development Approach. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, PAS-104(12), pp.3446-3452.
- Blum, M. and Wall, J. (1997). HRM: Managing conflicts in the firm. Business Horizons, 40(3), pp.84-87.
- Hook, C. and Jenkins, A. (2019). Introducing Human Resource Management. Harlow, United Kingdom: Pearson Education Limited.
- Ivancevich, J. and Konopaske, R. (2013). Human resource management. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Kramar, R. and Syed, J. (2012). Human Resource Management in a Global Context. Palgrave Macmillan.
- Leroy, H., Segers, J., van Dierendonck, D. and den Hartog, D. (2018). Managing people in organizations: Integrating the study of HRM and leadership. Human Resource Management Review, 28(3), pp.249-257.
Written by
Email: [email protected]
