Business world is very challenging and complicated. So to stay with full preparation and maintain a business properly it is important to learn about business law. As a responsible citizen of any independent country knowing about law and regulations are the duties of people. If the citizens know about law properly from Different Sources of Law there less crime will take place (Abbott, Pendlebury and Wardman, 2013). The paper is focused on the discussion about different business organization, their formation, funding, dispute solving procedure and overall review of law and procedures and how they work. The paper is very beneficial to learn and understand the business law in a easy way with examples.
Explain different sources of law
There are basically six sources of law commonly found. They are:
Case or Common law: Case or common law is originated from England. It refers to the laws which are made as precedents by judges. Rulings and decisions taken by the courts. They become binding for the jurisdiction’s system after that (Abbott, Pendlebury and Wardman, 2013). The lower courts need to stand by the previous decision of higher court for the future references which is similar in nature.
Statutory law: It is a law introduced by the legislative of the government. They can be modifying, change, abolish and delete as part or whole in the Common law. The powers of the legislature are secured and controlled by the constitution of that country. It is done to ensure that the laws cannot breach constitutional provisions (Claire Moore Dickerson and Janis Pearl Sarra, 2014).
Administrative law: Administrative laws are the source of law which is developed by different state agencies of the country with the power to perform and work according to those laws. Such as; Regulatory bodies/ agencies.
Court rules: Court laws established by the highest court of UK and the legislature. It is the way to provide make proper judgement and rules for treating with the criminal and civil procedures to work on court processes (Claire Moore Dickerson and Janis Pearl Sarra, 2014).
The constitution: The constitution is the supreme law of any country. It is not possible to pass or enforce any kind if law if they contradict or conflict with the Constitutions. It is the most important set of laws for all. It necessary, amendments to the constitution can be done depending on the procedural provisions given in the constitution. Sometimes in some countries it is important that the amendments go through a public referendum to change or do any kinds of modification (Macintyre, 2018).
The legal system: The UK is known as a constitutional monarchy. The Head of State is the monarch for the country whose duties, functions and powers are described and decided by the convention. One of the conventions of the monarch is to stay politically neutral. England and Wales both are operated based on the common law system. It is the combination of passing legislation and creating precedents through case law Claire Moore Dickerson and Janis Pearl Sarra, 2014). The laws are established by the passing of legislation in the Parliament operated with the House of Commons and the House of Lords. The House of Commons are elected by the people directly and the Prime Minister is the member of this House. The Court System and case law are controlled by the judiciary separated from the parliament.
Rule of law: The rule of law refers to the fundamental doctrine by every individual. They need to obey and submit to the law. In essence, there is no person is above law. The United Kingdom does not have a written constitution but the rule of law, with the Parliamentary Sovereignty and court rulings, define the principles of ‘unwritten constitution’ of UK law. The fundamental value and principles of rule of law are fairness, legal certainty, equality etc. Claire Moore Dickerson and Janis Pearl Sarra, 2014)
How laws evolve: The United Kingdom have no single document on British Constitution. There constitution formed by variety of documents made from hundreds of years. Their documents building on different legal precedent set by its predecessor. In recent times the acts of Parliament, treaties, common law court rulings, royal prerogative, and EU law etc. are also formed based on the British Law and constitution. The charter of liberties, Magne Carta, the petition of right, the bill of right etc. are the most important documents to work on the law of UK.
Who they protect: By the law, treaties and constitution they try to protect the people of the UK and ensure their right and responsibilities of law. The law also abides by the proper rules and regulations for the people of UK.
Separation of power:
Whereas the rule of law refers to the fundamental doctrine by every individual, then the separation of power refers to the separation of legal bodies to take necessary steps against criminal offence, or violation of laws.
Jurisprudence-Decay-Bentham: Bentham’s cosmopolitanism in its legal aspect, it is one of the important aspect of international jurisprudence. This article contributes in the role of universal jurisprudence doing the close assessment on the both its expository and censorial modes based on their cosmopolitan qualities
List of Laws:
- British Overseas Territories law (14 C)
- Scots law (30 C, 85 P)
- Welsh law (22 C, 16 P)
- Admiralty law in the United Kingdom (1 C, 10 P)
- Anti-discrimination law in the United Kingdom (2 C, 43 P)
- Alcohol law in the United Kingdom (30 P)
- United Kingdom banking law (1 C, 4 P)
- United Kingdom business law (3 C, 10 P)
- Civil law in the United Kingdom (4 C)
- Criminal law of the United Kingdom (6 C, 54 P)
- Currency law in the United Kingdom (11 P)
- Disability law in the United Kingdom (1 C, 10 P)
- Election law in the United Kingdom (1 C, 52 P)
- United Kingdom enterprise law (1 C, 15 P)
- Emergency laws in the United Kingdom (23 P)
- Environmental law in the United Kingdom (35 P)
- Family law in the United Kingdom (4 C, 36 P)
- Health and safety in the United Kingdom (3 C, 47 P)
- Human rights in the United Kingdom (23 C, 33 P)
- Insolvency law of the United Kingdom (2 C, 37 P)
- Immigration law in the United Kingdom (3 C, 27 P)
- United Kingdom military law (1 C, 59 P)
- Property law of the United Kingdom (5 C, 21 P)
- United Kingdom public law (1 C, 11 P)
- Transport law in the United Kingdom (2 C, 8 P)
Explain the role of government in law- making and describe how statutory and common law is applied in the justice courts
Government and parliamentary structures are the different branches of government which plays important roles in the making of laws.
Role of government in law- making
Stage one – Ruling party provides vision, goals and direction
At the time of major conferences policies are made by the ruling party based on the debate and discussion. At these conferences particular issues are discussed and the party decides overall vision, goals and direction of the issue.
Stage two – Ministers draws up policy on an issue
Stage two takes place at national level where the ruling party tries to convert official government policy or law by the Constitution. The ministers of the government attempt to develop new policies and laws to approve for making legal effect to the policies. But it is a long and slow process because the proposed law of ruling party is debated and negotiated among different parties (Macintyre, 2018). In the meantime, drafts are prepared to proposed and discussed in the parliament by ruling party.
Stage three – Finalizing a policy
After all the discussion when the policy is finalized by the relevant Department and Ministry the issues and options are prepared in a final policy published as a White Paper. The White Paper refers to the statement of intent and a detailed policy plan. Finally, again it is debated and adopted by Parliament and approved by Cabinet members after completing the discussion proceedings (Macintyre, 2018).
Stage four – Passing a law
A White Paper is considered as the basis of legislation. The Department or the ministers can decide on the new law to achieve its objectives and implement it to work on drafting the new law. In its early stages before becoming a new law it is referred as a draft Bill.
Stage five – Subordinate legislation and implementing the law and policy
After passing a law by National Parliament it become published. So the national, provincial ministries will be responsible to implement the law everywhere. National, provincial legislatures and local authorities will pass subordinate legislation in the new original law (NESTERUK, 2014).
Application of statutory and common law in the justice courts
Common law and statutory laws both are used in most nations for justice to be served. The importance of these laws is many. The laws which are made based on the new decisions of judges in courts are common law and Laws which are issued by various government agencies are statutory law.
Common laws are used for making further judgment in the similar ways of justice courts. The judgment of higher court is used as the law to support the similar kinds of case. With the existing common law there are no statutes so the other judges interpret the existing law and determine new boundaries and distinctions for different court procedures. The opinions of higher courts are become binding on future decisions of lower courts (NESTERUK, 2014). It helps to make the judicial process relatively fast based on the established framework to base ruling. But some bad decision made by a higher court make the rules reluctant to overrule previous decisions in case of common law.
The basis of precedent is dealt with by Obiter dictum, that is by the way and the actual binding decision being rationally deciding, or the reason for the decision.
Statutory laws are made for the citizens to resolve their many issues, and formalize a law for their betterment. They cover all areas of law regulated by statutory exclusively. There are some cases where common laws are not applicable. So for such special cases statutory laws are used.
The judges interpret laws by using certain rules called the golden, mischief and literal, an example of this usage is a case called Fisher v Bell, here a shop owner had a knife for sale in his window, he was arrested for offering for sale an offensive weapon, the court said it was not an offer but an invitation to treat, so the court applied the law literally (NESTERUK, 2014).
Below is a diagram of how Parliament makes laws and the court structure of England and Wales
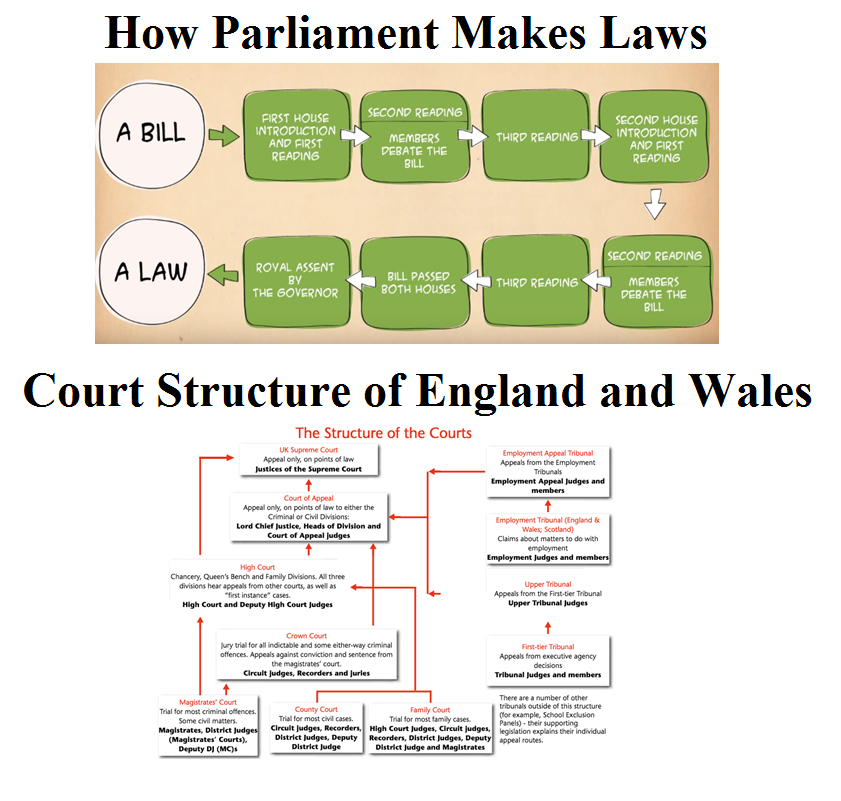
The above shows the courts and the details of the judges who sit in the various courts.
Use specific example illustrate how company, employment and contract law has a potential impact on business
There are three aspects of law which can impact on business from different aspects. They are
Company law helps to regulate the incorporation of a company. It focuses on how a company can conduct its business, how they design their structure and function. The company law also emphasizes on what compliances or filings are need to be done in the company with the respective government and other statutory agencies for maintaining the transparency among different organizations. So Atlantis must have a registered office and file annual accounts
Employment Rights Act 1996
Employment laws are used for non-discrimination and non-exploitation matters of employees, laborers and workers. It is the law works with designing and regulating the work of weekly hours, minimum wages, working conditions, health and safety and others related aspects which can affect different policies of employees (Schaffer, Agusti and Dhooge, 2015). So Atlantis must give its employees details of their pay, place of work, hours amongst other, they must pay minimum wage, also comply with the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974.
Contract law is the law which regulates how legal entities such as companies, partnership, and the firm will execute the contracts to avail the business services. It is focused on dealing with documentation of the business.
A contract is an agreement between two or more parties who have a common intention to be bound by their promises to each other.
The contract is made up of:
- Intention
- Offer
- Acceptance
- Consideration
- Capacity
For example, if we at Atlantis do anything with any other party this identity will all be handled by contract law.
Similarly, company law takes care of the company’s function, policy, rules and regulations to make the overall protection of the organization and make the company run their business functions smoothly (Schaffer, Agusti and Dhooge, 2015). It helps to protect and secure the company in any problems or barriers.
Finally, the employment law is the commitment among the employees and employer of the Parker Ltd. Here the company promised to take care of their employees and employees also provide the commitment to serve the company with their best efforts.
If any disruption in legal procedure takes place all of the law helps to protect the victim party abide by the law and commitment. Any legal steps can be taken based on these laws.
Explore how different types of business organizations are legally formed
To
The Board of Directors of Atlantis
From Emilia
Re: Report on various areas of such as company, contract and legal solutions.
Dated: 25th December 2019
There are different types of business organizations can be seen which are formed with the help of different types of laws. Companies are classified by various names which are given below They are:
Partnership: Partnership firm is formed with two or more partners within the partnership law. According to the Section 4 of Partnership Act, 1932 partnership business is formed. The law says that, the relation between persons who have agreed to share the profits and carried the business activities by all or for all. It is an agreement among two or more persons to carry lawful business by sharing profits and abide by all the liabilities occurred from the business. Persons who enter into such agreement are known as partners (Spiller, 2010).
The Partnership Act, 1932 help to do the registration of firms with the Registrar who is appointed by the Government. The registration of a partnership business is not compulsory but it can help the business to protect from different bindings of business law.
Limited Liability Partnership: According to the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, the partnership corporate body is formed and incorporated the Act. It is a legal entity separate from the business members of limited liability partnership business.
Charities: For setting up a charity the authority of the charity need to apply to the register the organization with the commission. It should be register in the name of charitable incorporated organization and its annual income need to be more than £5,000, unless it is a specific type of charity they do not have to register. The commission will take action based on the secure compliance whether the charity should be register or not.
Limited company: The best type of company we can set up is the small basic limited company, if is successful we can float it on the stock exchange. We should trade with a limited or PLC Company, as the owners will probably be more professional as they have taken the trouble of setting up a company to trade.
How to set up the company: The Company need to set up based on the company rules. They need to choose the name first. Then they need to choose a name for the company and select directors and secretary. Then they need to decide who will be the shareholders or guarantors and identify people to take control over the company. They need to prepare documents agreeing how to run the company and check the records and register the company at the end. Finally, after register process the organization can proceed for business (NESTERUK, 2014).
To appoint authority directors and shareholders they need to sell the company share among public and select the highest shareholders to set up board of directors who will run the company on behalf of all the shareholders. Here the authority of the company will set up the business for the function of the organization.
Role of shareholders: Shareholders will perform the role of the owners and also identify the company functions and policy time to time. They will take care of the company’s function and keep their share intact by concentrating on the policy of the business.
Explain how business organizations are managed and funded
The business organizations are different from each other. So the management and funding process of business are also different. Here the overall management and funding of the business organizations are discussed:
Sole proprietorship: It is a business managed by only an individual. As the legal procedures are not necessary to start the business any one can start it anytime with little funding (Stoltenberg, 2008). All the business work of sole proprietorship is done by the family members or friends or the business owner handle everything alone. The fund of the business managed by friends, family and relatives or from personal loans.
Partnership Business: Partnership business has two or more than two owners. The business needs to collect their funding from their partner’s pool of capital or they can take loan from the banks or any other sources. Here partnership business organizations are responsible to manage the business activities by their partners. It depends on how the deed of the partnership is prepared (Stoltenberg, 2008). All the business decisions are made by the business partners and they are all responsible for the business liabilities. It has no separate identity like company or corporation business. So the partners need to deal with liabilities along with the business profit issues.
PLC Corporations: A corporation has a unique separate entity from their owners. In the company or corporation business it can be taxed, sued and enter into contractual agreements in the name of the business. The management of the business is managed by the board of directors. There are many employees and shareholders are involved. It can be a public limited company or private limited company (Systems, organizations, analysis, management, 2012). The fund of the business is collected from share market by selling business shares among the general people. The management of business is maintained and controlled by the business memorandum.
Company Liquidation: Liquidation is a procedure used to wind up companies. It requires many forms in each case the liquidator perform the duty to collect and realize the assets of the company. The overall procedure is performed for the distribution to its creditors to meet up their debts. The company liquidation can take place in certain situations where the company is unable to pay debts or the value of the company’s assets is less than their liabilities (NESTERUK, 2014). For liquidation, a liquidator can be appointed to resolve the liquidation of the organization.
In liquidation, there are many liquidators are appointed to take over the management and realizes assets for the creditors. They can trade in some limited circumstances for the business purpose. In compulsory liquidation, the court works as a gate keeper to commence the process. In voluntary liquidation procedure takes outside of the court by resolution of the company’s shareholders by involving the court.
Recommend legal solutions for resolving a range of disputes using example to demonstrate how a party might obtain legal advice or support
Alternative dispute resolution is the way of resolving disputes between consumers and traders without involving the court. The government encourage the development of ADR. The common forms of ADR are:
- Mediation
- Arbitration
In the UK, there are many large and well-established ADR schemes in regulated sectors. They are financial services, energy and telecoms process. Outside the regulated sectors, many businesses organizations are members of voluntary ADR schemes (Abbott, K., Pendlebury, N. and Wardman, K, 2013).
Basically there are three ways to settle down disputes. The commonly used methods are:
Negotiation: People who disagree to discuss the problem but want a mutual agreement here the negotiation starts. When people try to solve problem and ready to find out a solution which can fulfill their best needs and interests.
Solving problems with the help of negotiation is easy and important to do. For instance, in a situation where Partners of the business get into a fight about business management such problems can be solver be negotiation. Effective negotiation skills and methods improve negotiating techniques of individuals.
Mediation: People involved in dispute scan take help from mediator. They are the unbiased and impartial person to process the negotiations. When negotiations fail to resolve any problem, the mediator help to resolve it by encouraging discussion among the parties. The mediator helps them to resolve the problem which results in in a “win-win” situation for everyone (Systems, organizations, analysis, management, 2012). It also makes the parties satisfied with the result. Participation in mediation can be voluntary.
For example, some courts make some cases referred to mediation for trial. Here the mediator tries to settle the dispute but can help the parties to solve their problems.
Mediation helps the parties reach an outcome for everyone’s satisfaction. Courts are limited in the remedies to solving disputes and problems among the parties. The cost of mediation divided between the parties. The lawyers can present at the time of mediation process (Nesteruk, 2014).
Arbitration: In arbitration process here a neutral person or panel focus on the facts and issues and find out a solution to solve problems. Arbitrators are experts in some particular law or industry, to make an effective and knowledgeable decision. The arbitrator or panel is usually chosen by the parties together or they each can choose an arbitrator, and the two arbitrators will then choose a third to make a panel of three (Systems, organizations, analysis, management, 2012). With the overall setup arbitration process works to solve the disruption among the parties.
Conclusion
Business law is a very interesting subject to learn and get to know about a lot of things about business. It is one of the best way to learn about the business formation and their way of maintenance in the long run. From the overall discussion the management of law and how does that work can also be identified (Nesteruk, 2014). So it is very important for each and every business individual to learn and understand business law for the future betterment.
References
- Abbott, K., Pendlebury, N. and Wardman, K. (2013). Business law.Andover: Cengage Learning.
- Claire Moore Dickerson and Janis Pearl Sarra (2014). Challenging borders in business law: the scholarship of Claire Moore Dickerson. Vancouver, Canada: University of British Columbia Faculty of Law.
- Macintyre, E. (2018). Business law. Harlow, Essex, United Kingdom; New York: Pearson.
- NESTERUK, J. (2014). THE MORAL DYNAMICS OF LAW IN BUSINESS. American Business Law Journal, 34(2), pp.133–140.
- Schaffer, R., Agusti, F. and Dhooge, L.J. (2015). International business law and its environment. Stamford, Ct: Cengage Learning.
- Spiller, D. (2010). International Organizations and their effect upon the libraries of developing countries. International Library Review, 11(3), pp.341–351.
- Stoltenberg, C.D. (2008). LAW, REGULATION AND INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS. American Business Law Journal, 40(3), pp.445–457.
- Systems, organizations, analysis, management. (2012). Business Horizons, 12(2), pp.93–95.
