Introducing E Governance in Bangladesh for Improving Public Service Delivery
Brief Background
This study will be demonstrating on the introducing E governance in Bangladesh for improving public service delivery. The practice of E Governance is now globally acclaimed for increasing accountability and transparency of public services, rendering faster and smoother services to all citizens in Bangladesh, and fostering economic growth. Though there are some challenges like lack technologic knowledge, inadequate human resources capacity or social challenges, still there is a hope to overcome those challenges. Therefore, it would be possible to achieve the goal of Vision 2021 in terms of developing Digital Bangladesh.
Introduction
E-governance is a very effective mechanism in terms of service delivery. E-governance is equivalently related with good governance and it is being practiced by all developed countries. In that case, the E-governance practice in Bangladesh is a new mechanism and it is an urge mechanism for making successful the vision 2021 in response to Digital Bangladesh. There are so many reasons for introducing E-governance in Bangladesh public services. Though, there are so many challenges for implementing E-governance practice in Bangladesh, still it has so many benefits, that’s why it would be necessary to introduce the practice of E-governance in Bangladesh as early as possible (Brown, 2005).
There are 4 types of E-governance
- Government-to-Citizen (G2C): It is interaction between government and citizen in which citizens have easy access to get the government services from anywhere.
-
Government-to-business (G2B): It is government services between Government and Business in which organizations gave easy access to get the government services like licensing or government registration.
-
Government-to-Government (G2G): It is fully related with all government activities among the government department and agencies to increase the efficiency of government process.
-
Government-to-Employee (G2E): It is the internal part for providing online facilities to all employees in response to leave applications, salary review, training and development.
Three reasons for introducing e-governance in public service delivery
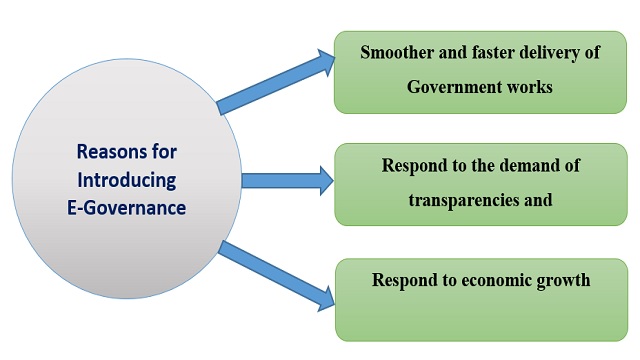
Fig: Reasons for introducing e-governance
- Smoother and faster delivery of Government works
For making successful the vision of Digital Bangladesh, there is no alternative of using of e-governance because it will support for fast and effective delivery of public services. To provide better services, the prospect of e-governance is significant because it eliminates middlemen between the clients and authorized who is responsible for giving the service (Rahman, 2016).
- Respond to the demand of transparencies and accountabilities
The best suited reason for applying e-governance system in public services is about transparency and accountability for the task. Transparency will show that there is no illegal transaction for getting a service. Accountabilities will show that the responsible person is obliged to report higher authority for his assigned task. The vision of Digital Bangladesh would not be successful if the aspect of transparency and accountability is not properly maintained (Rahman, 2016).
- Respond to economic growth
E-Governance is very fruitful for reducing corruption in public administration because all the services like e-registration, e-tax, e-tender, e-education and other digital services are occurred in transparent ways. It is such a mechanism in which everything will done through online. The online support system is very much effective for responding to economic growth in which corruption reduces to achieve economic objectives (Rahman, 2016).
Three major challenges to implement E Governance
This is not an easy task to implement e-governance practices over a night because there are some challenges those create obstacle. These are as follows:
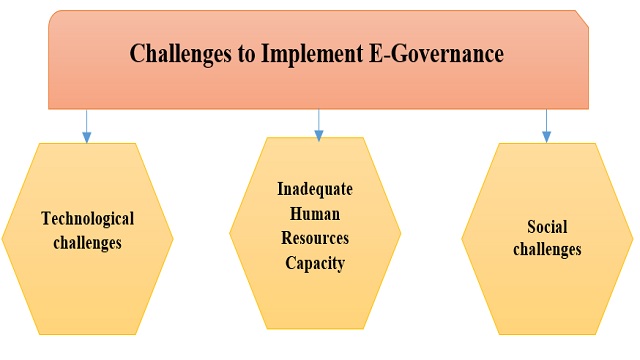
Fig: challenges to implement e-governance
- Technological challenges
There are some technological challenges in delivering public services for introducing the concept of e-governance because most of the public officers in Bangladesh have lacking in computer knowledge, computer operation, IT knowledge, and office application in computers. There have also problem in ICT infrastructure development, privacy issues and data security. Cybercrime is also a threat for implementing e-governance just because of poor security system (Mahbubul Alam, 2018).
- Inadequate Human Resources Capacity
In Bangladesh, there have not so many trained people who can support for spreading the technological knowledge, sharing the importance of e-governance. Specially, outside Dhaka city, this situation is very alarming (Mahbubul Alam, 2018). It is only reason for having Inadequate Human Resources Capacity to train more than 10 lac people within vision 2021.
- Social challenges
Social challenges may include digital divide, culture, and income. The gap in accessibility of internet and accessibility of computer all over the country will show digital drive as obstacles. If the internet price is increased and computer or mobile price is increased, it will be gone beyond to the purchase ability. The cultural implication of new technologies may create barrier in public services due to cultural differences (Mahbubul Alam, 2018).
Conclusions and Recommendations
Transparency, Accountability, administrative reform, decentralization, and satisfaction of public service by public officers are key problem areas in the present governance system in Bangladesh. Though, there have technological challenges, social challenges and human resource challenges, it would be recommended to arrange so many training program to train all the government staff, adapt them with new culture as well as cultural diversity. It should be trained a huge number of people who will teach the general people in or outside Dhaka. Government should work on to eliminate data hacking or cyber-attack by applying strong security systems (Gupta, 2004).
References
Brown, D., 2005. Electronic Government and Public Administration. International Review of Administrative Sciences, 71(2), pp. 241-254.
Gupta, M., 2004. Towards E-Government Management Challenge. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill .
Mahbubul Alam, K. A. M. A. I., 2018. E-Governance: Challenges and Opportunities. International Review Journal, pp. 05-06.
Rahman, M. L., 2016. E-Governance and Bangladesh. [Online]
Written by
Email: [email protected]

